
Comparatives and Superlatives in English
¿Quieres saber cómo utilizar los comparativos y superlativos en inglés? Te lo cuento todo en este MEGAPOST. It’s the best! ¿Ves? ¡Esto es un superlativo! 😎

Table of contents
One of the grammatical points that is repeated in all the syllabi I work with today in my English academy is that of **comparatives and superlatives in English**. Already at an A2 level, students begin to learn to **compare** and to **use superlatives**, as it is something we do in English all the time.
So, how about starting 2019 with KSE Academy learning about comparatives and superlatives in English? Plus, I’m giving you a **PDF** to download and study whenever suits you.
As you well know, **comparatives** are used to say that something is more or less *whatever*, or even the same as, another thing. And **superlatives** are used to say that something is *the most of the most* or *the least of the least*.
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives in English
Comparative adjectives in English can occur in three forms:
- **Comparatives of superiority:** to say that something is more *whatever* than another thing.
- **Comparatives of inferiority:** to say that something is less *whatever* than another thing.
- **Comparatives of equality:** to say that two things are equally *whatever*.
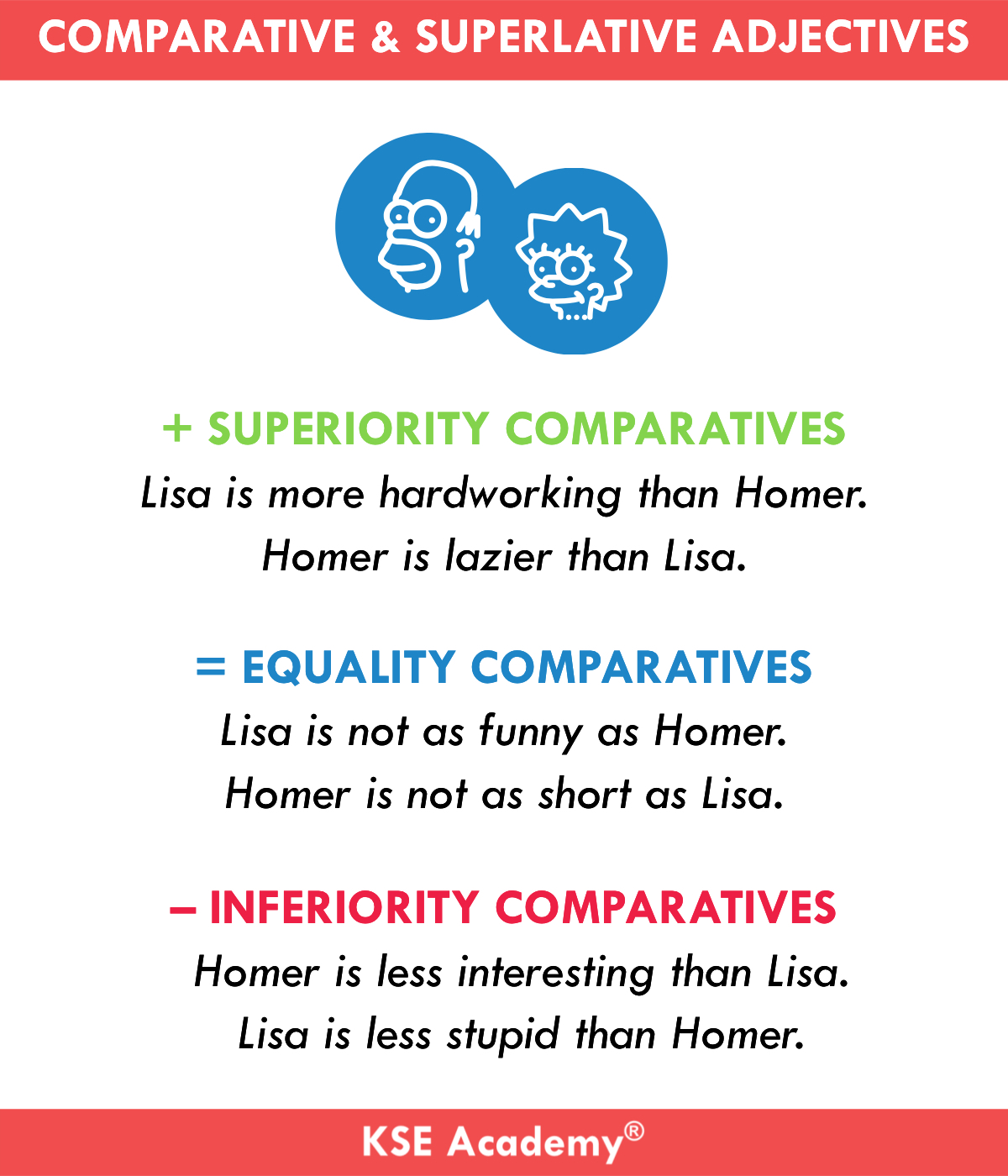
Let’s look in more detail at each type of comparative and how they are constructed.
Comparative Adjectives of Superiority
To express superiority in English with a comparative, we have two options:
- **Add -er to the end of the adjective:** this is done when it’s a 1-syllable adjective, or a 2-syllable adjective ending in -y.
- **Add more before the adjective:** when it’s an adjective of 2 or more syllables.
- Superlatives follow the same rules but we change **-er** to **-est** or **more** to **the most**.
| ADJECTIVE | COMPARATIVE | SUPERLATIVE |
| fine | finer than | the finest |
| big | bigger than | the biggest |
| lazy | lazier than | the laziest |
| difficult | more difficult than | the most difficult |
Other things you should know are:
- If a one-syllable adjective ends in a **consonant-vowel-consonant** pattern, we double the last letter before adding **-er**.
- After the comparative, **than** is added if another element follows.
Example of comparative and superlative sentences of superiority:
This is **the finest** wine I’ve ever tried.
He’s **the most intelligent** student in the class.
My hair is **longer than** yours.

Exercise on Comparative Adjectives of Superiority
Now try this simple **exercise on comparatives in English**. Click on Shuffle and then in Options select Definition as the Answer. Now let’s see if you can form the comparatives of superiority for these 15 simple adjectives.
Comparative Adjectives of Inferiority
Comparative and superlative adjectives of inferiority are very easy to construct, as we don’t need to change the word itself.
To express inferiority in English you simply need to:
- **Add less before the adjective:** this is done for comparing with all adjectives, regardless of their length.
- For superlatives of inferiority, we simply change **less** to **the least**.
| ADJECTIVE | COMPARATIVE | SUPERLATIVE |
| fine | less fine than | the least fine |
| big | less big than | the least big |
| lazy | less lazy than | the least lazy |
| difficult | less difficult than | the least difficult |
Other things you should know are:
- After the comparative of inferiority, **than** is also added if another element follows.
- The adjective never changes when expressing inferiority.
Example of comparative and superlative sentences of inferiority:
That was **the least expected** result.
Jim is **less hardworking than** his sister.
Bob is **the least skilled** in the family.
Comparative Adjectives of Equality
**Comparisons of equality** are also very easy to construct. We simply add **as** or **so** before and after the adjective, without changing the adjective.
| ADJECTIVE | COMPARATIVE | SUPERLATIVE |
| fine | as/so* fine as | – |
| big | as big as | – |
| lazy | as lazy as | – |
| difficult | as difficult as | – |
*so = only in negative sentences
Example sentences with comparative adjectives of equality:
John is still **as silly as** when he was a kid.
I thought the test wasn’t **as tough as** the last one.(negative sentence with **as**)
My hair is **not so long as** yours.(negative sentence with **so**)
Irregular Comparative Adjectives
In English, there are 3 adjectives whose comparative and superlative forms are irregular. These are shown in the following table:
| ADJECTIVE | SUP. COMPARATIVE | SUPERLATIVE |
| good | better than | the best |
| bad | worse than | the worst |
| far | further / farther than | the furthest / farthest |
Examples of comparative sentences with irregular adjectives:
This is without a doubt **the best** performance he’s given in a while.
He’s **better than** me at football.
They live in **the farthest** village in the whole county.
However, when we use these adjectives to express inferiority, irregular adjectives behave like other adjectives:
| ADJECTIVE | INF. COMPARATIVE | SUPERLATIVE |
| good | less good than | the least good |
| bad | less bad than | the least bad |
| far | less far than | the least far |
The same happens with comparisons of equality, where irregular adjectives follow the same pattern as the rest:
| ADJECTIVE | EQUALITY | SUPERLATIVE |
| good | as good as | – |
| bad | as bad as | – |
| far | as far as | – |
VIDEO: Comparatives and superlatives in English: Adjectives
Comparative and Superlative Adverbs in English
Comparative adverbs in English, like adjectives, can occur in three forms:
- **Comparatives of superiority:** to say that something is done in a more *whatever* way than another thing.
- **Comparatives of inferiority:** to say that something is done in a less *whatever* way than another thing.
- **Comparatives of equality:** to say that two things are done with the same degree of *whatever*.
Let’s look in more detail at each type of comparative and superlative adverb, and how they are constructed.
Comparative Adverbs of Superiority
If you already know how to compare with adjectives in English, doing so with superlatives is a piece of cake. The rules are almost the same:
- **Add -er to the end of the adverb:** this is done when it’s a 1-syllable adjective.
- **Add more before the adverb:** when it’s an adverb of 2 or more syllables.
- Superlatives follow the same rules but we change **-er** to **-est** or **more** to **the most**.
The only difference from comparing adjectives is that in this case, **-er** is only added to one-syllable adverbs; those ending in **-y** are not included.
Look at the following table:
| ADVERB | COMPARATIVE | SUPERLATIVE |
| fast | faster than | the fastest |
| often | more often than | the most often |
| quickly | more quickly than | the most quickly |
Let’s look at some examples with comparative adverbs of superiority:
He usually drives **faster than** me.
We need to think about this **more carefully**.
I visit my grandparents **more often than** before.
Exercise on Comparative Adverbs of Superiority
Now try this simple **exercise on comparative adverbs** in English. Simply think of the answer you need to fill in the blank and then click to flip the card.
Comparative Adverbs of Inferiority
Comparative adverbs of inferiority work the same way as adjectives. Look at this table:
| ADVERB | COMPARATIVE | SUPERLATIVE |
| fast | less fast than | the least fast |
| often | less often than | the least often |
| quickly | less quickly than | the least quickly |
Let’s look at a couple of examples of sentences with comparative adverbs of inferiority:
He should do exercise **less frequently**; he’s going to get injured!
I can write with both hands, but **less easily** with my left one.
Comparative Adverbs of Equality
Comparative adverbs of equality are constructed in the same way as adjectives of equality:
| ADJECTIVE | COMPARATIVE | SUPERLATIVE |
| fast | as fast as | – |
| often | as often as | – |
| quickly | as quickly as | – |
Examples of Comparative Adverbs of Equality:
I can’t speak French **as quickly as** you.
She danced **as beautifully as** ever.
Irregular Comparative Adverbs
In English, there are 2 adverbs whose comparative and superlative forms are irregular. These adverbs are **well** and **bad**:
| ADVERB | SUP. COMPARATIVE | SUPERLATIVE |
| well | better than | the best |
| bad/badly | worse than | the worst |
However, when expressing inferiority and equality, they do not undergo any change:
| ADVERB | INF. COMPARATIVE | SUPERLATIVE |
| well | less well | the least good |
| bad/badly | less bad than* | the least bad* |
| ADVERB | EQUALITY | SUPERLATIVE |
| well | as well as | – |
| bad/badly | as bad as* | – |
* **bad** sometimes acts as an adverb of the adjective **bad** in American English, although it’s more common to use **badly**.
Example of comparative and superlative sentences with irregular adverbs:
I hadn’t done the assignment **as well as** I thought.
Luke didn’t fail, so I guess he did it **better than** he thought.
How to Compare Nouns in English
To create comparisons using nouns, we usually use the words **more, less** and **fewer**. **More**, obviously, means more; **less** and **fewer** mean less, but **fewer** is used with countable nouns and **less** with uncountable nouns.

There are **more people** here today **than** yesterday.
I have **less money than** I thought. (**money** is uncountable)
Liam has **fewer things** to do now that he’s lost his job. (**things** are countable)
More and more, less and less and fewer and fewer
In English, when we want to express that the quantity or number of something is growing or decreasing over time, we can repeat the comparative. We can do this with adjectives (The population was getting **bigger and bigger**), with adverbs (He was speaking **more and more** quickly) or with nouns and the words **more and more**, **less and less** and **fewer and fewer**.
There are **more and more** people studying English nowadays.
Every week I feel I have **less and less** free time.
He comes by **fewer and fewer** every year.
Most, least and fewest
Similarly, we can use **(the) most, (the) least** and **(the) fewest** with nouns to create superlative sentences, similar to superlative sentences for adjectives and adverbs.
The person who writes **the most words** gets the prize.
This politician got **the most votes** in the last election.
The person with **the least money** eats for free. (**money** is uncountable)
The worst teachers usually have **the fewest students**. (**students** are countable)
As you can see, we use **least** with uncountable nouns and **fewest** with countable nouns.
How to Use the same
In English, we use the word **same** when two things are identical or share a characteristic. We can use **same** before a noun or as a pronoun:
Joe and I were looking in **the same direction**.
Both jackets look exactly **the same**.
How to Compare with the same as
Sometimes, we can use **the same (…) as** to mean “the same as” or “equal to” another thing. For example:
He told me exactly **the same story as** her.
Luke studied **the same as** his sister.